Introduction: The Old Golden Root Supported by Modern Science
Haldi, or turmeric (Curcuma longa), is one of the most studied medicinal plants in both traditional and modern medicine. Because of its bright color and powerful healing properties, turmeric has been an important part of Ayurveda, Siddha, and Traditional Chinese Medicine for thousands of years.  Today, scientific research has confirmed many of these traditional claims. For example, it has been shown that turmeric contains strong bioactive compounds, especially curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory effects. Because of this, turmeric is used to treat disorders related to inflammation, improve skin health, boost immunity, and promote overall physical resilience. This article talks about the scientifically proven ways that turmeric can heal naturally. It is also easy to read, good for SEO, and good for your audience.
Today, scientific research has confirmed many of these traditional claims. For example, it has been shown that turmeric contains strong bioactive compounds, especially curcumin, which has anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, antimicrobial, and immunomodulatory effects. Because of this, turmeric is used to treat disorders related to inflammation, improve skin health, boost immunity, and promote overall physical resilience. This article talks about the scientifically proven ways that turmeric can heal naturally. It is also easy to read, good for SEO, and good for your audience.
🌿 The Science and Bioactive Components of Turmeric
Turmeric contains a lot of different phytochemicals, each of which helps it work as a medicine. Curcumin, a polyphenolic compound that gives the rhizome its bright yellow color, is the most important of these. Curcumin is one of a group of molecules called curcuminoids. Other members of this group are demethoxycurcumin and bisdemethoxycurcumin. These molecules have strong biological effects, especially when it comes to changing the pathways that cause oxidative stress and inflammation. Turmeric has volatile oils like turmerone, atlantone, and zingiberene in addition to curcuminoids. These oils have antimicrobial and anti-inflammatory properties that work well with curcuminoids.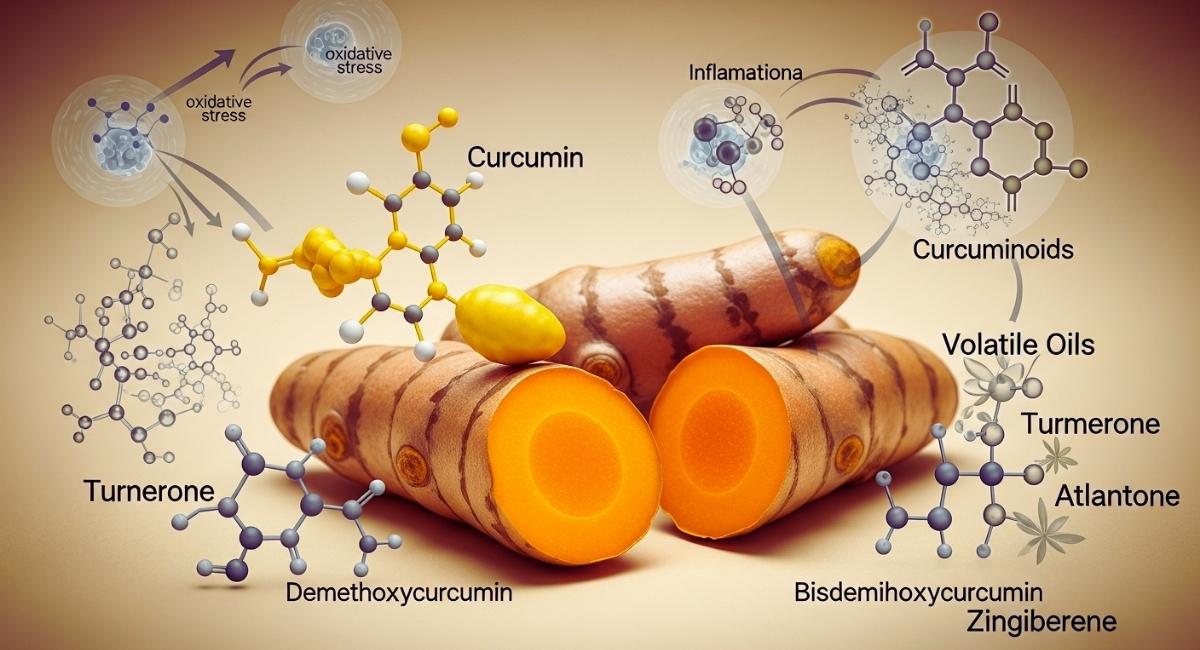
Curcumin functions biochemically by engaging with various molecular targets. It affects transcription factors like NF-κB (nuclear factor kappa-light-chain-enhancer of activated B cells), cytokines like TNF-α (tumor necrosis factor-alpha) and IL-6 (interleukin-6), and enzymes like COX-2 (cyclooxygenase-2) and LOX (lipoxygenase). Curcumin helps control inflammatory responses, lower oxidative damage, and boost antibody production by changing these pathways. Contemporary pharmacological research underscores curcumin’s potential in the prevention of chronic diseases, encompassing conditions such as arthritis, metabolic syndrome, anxiety, and dermatological issues like eczema and acne. Curcumin’s bioavailability is naturally low, but mixing it with piperine from black pepper or eating it in lipid-based foods makes it much easier for the body to absorb.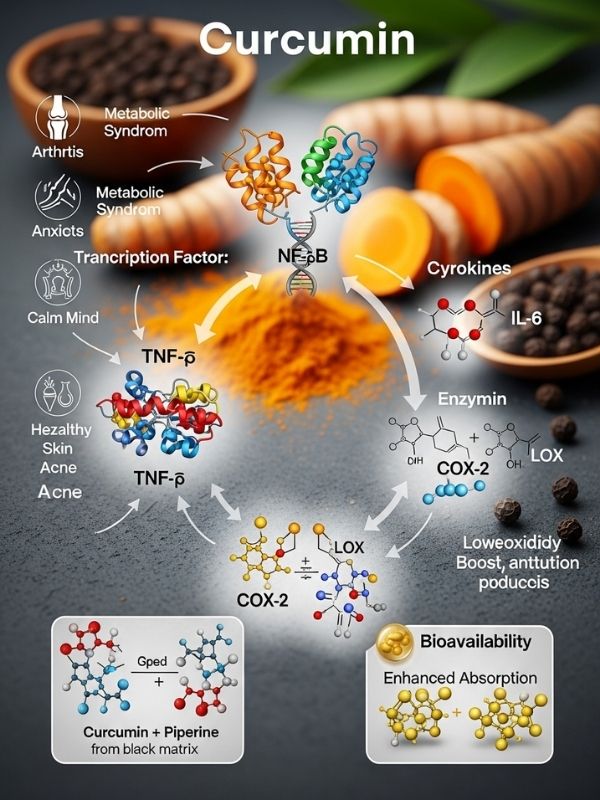
🟢Turmeric as a Natural Modulator of Chronic Inflammation: Its Anti-Inflammatory Action
Inflammation is a normal bodily process that is important for healing tissue and protecting the immune system. But long-term low-grade inflammation is linked to a number of modern health problems, such as arthritis, heart disease, neurodegenerative disorders, and metabolic dysfunction. Turmeric is especially important in the field of anti-inflammatory science, where curcumin works like synthetic anti-inflammatory drugs but doesn’t have as many bad side effects.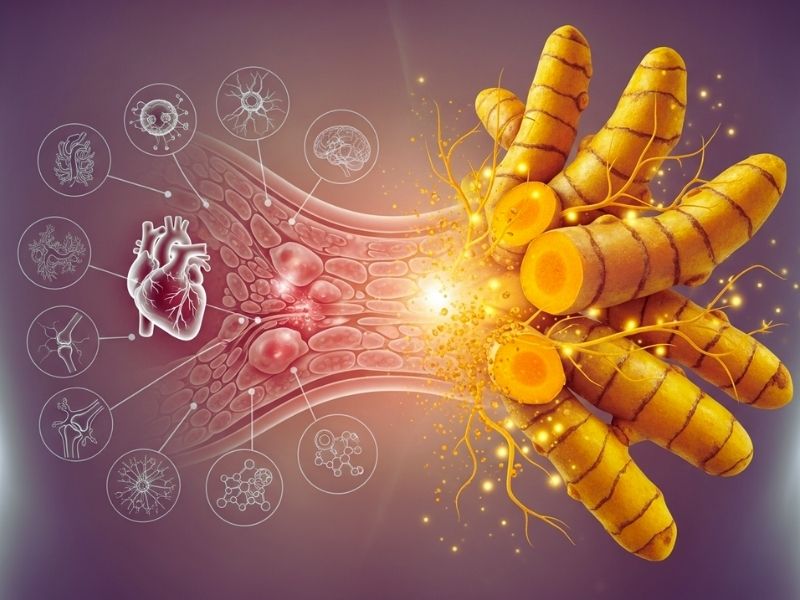
Curcumin reduces inflammation by lowering the levels of pro-inflammatory mediators like IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6. It also stops NF-κB, a transcription factor that controls how many inflammatory genes are turned on. Curcumin helps the body stay in balance by blocking this pathway and lowering too much inflammatory signaling. Curcumin also changes the COX-2 enzyme, which lowers the production of prostaglandins that cause pain, swelling, and inflammation. Its ability to fight free radicals also stops tissue damage, which can lead to inflammatory cascades.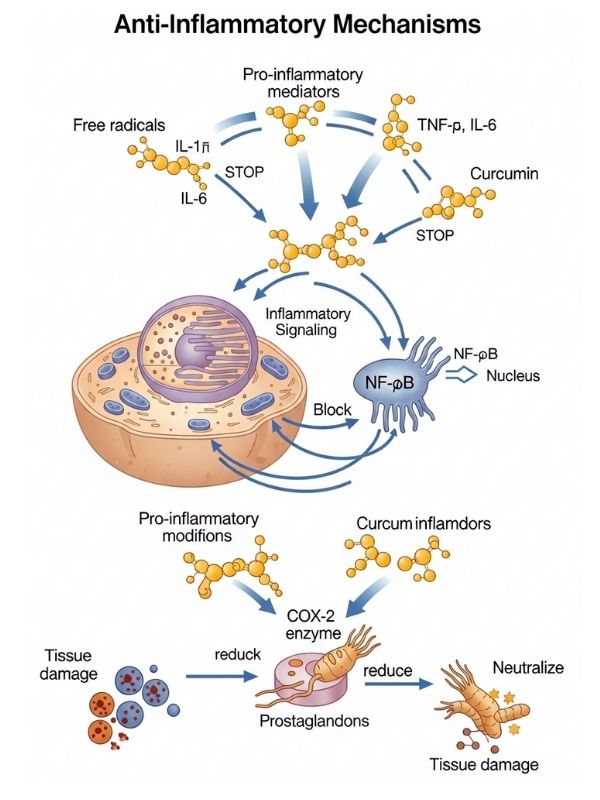
Clinical studies indicate that consistent intake of curcumin may ameliorate symptoms in patients with rheumatoid arthritis, osteoarthritis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Turmeric is better than steroid-based or NSAID medications because it doesn’t irritate the stomach or cause other problems in the body. Turmeric is a useful dietary supplement because it can naturally regulate the body. It helps keep joints flexible, reduces muscle soreness, and boosts the body’s overall ability to fight inflammation.
🔥 Turmeric is good for your skin because it kills germs, fights free radicals, and helps skin heal
The skin is the body’s largest organ and protects it from stressors, pathogens, and oxidative damage from the outside world. People have used turmeric for a long time in traditional beauty routines and dermatology because it cleanses, brightens, and heals. Modern science backs up these old ways of doing things by showing that turmeric is good for skin health because it has antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and wound-healing properties.
Curcumin’s antioxidant properties neutralize free radicals that come from UV rays, pollution, and metabolic processes. This protects skin cells from oxidative stress and early aging. It stops elastase and collagenase enzymes from breaking down structural proteins, which helps keep the skin firm and elastic. Turmeric’s antimicrobial properties, which are due to compounds like turmerone and curcumin, help stop the growth of bacteria that cause acne, like Propionibacterium acnes. This reduces breakouts and inflammation.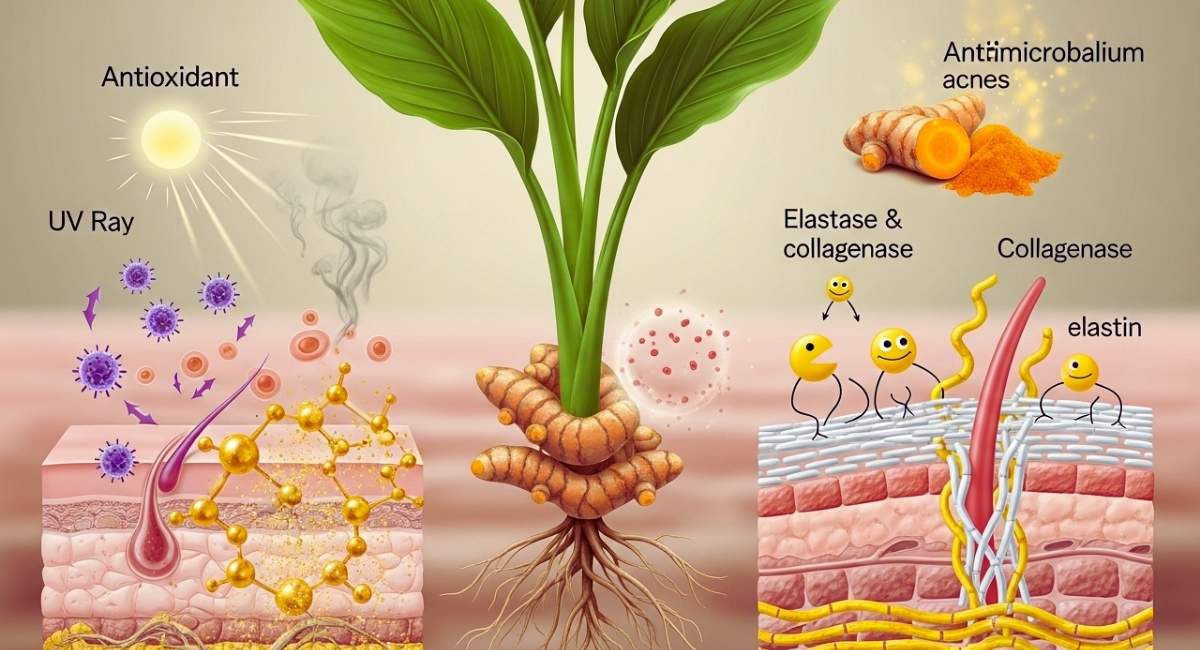
Curcumin also helps wounds heal by increasing the amount of collagen that is deposited, remodeling tissue, and making cells grow. The fact that it can reduce hyperpigmentation is because it stops the enzyme tyrosinase from making melanin. Turmeric is good for dark spots, acne scars, and skin that isn’t even in color. Turmeric can be used as a paste on the skin, mixed with natural carriers, or eaten. It makes the skin healthier and more radiant by improving barrier function and lowering inflammation.
🍃 Curcumin as an Immunomodulatory Agent: Boosting Immunity
The immune system is a complicated network of organs, cells, and signaling molecules that keeps the body safe from infections, toxins, and abnormal cell growth. Turmeric is known to be a strong immunomodulator, which means it helps control immune responses instead of just making them stronger. This fine-tuning effect is important because having too much immune activity (autoimmune disorders) or not enough immune activity (recurrent infections) can both be bad for health.
Curcumin boosts the immune system in a number of ways. It makes macrophages, T-cells, B-cells, and natural killer (NK) cells work harder. These cells are all very important for finding and getting rid of pathogens. Its antioxidant properties help the immune system by lowering oxidative stress, which can otherwise make the immune system work less well. Turmeric also helps the body make antimicrobial peptides, which boost its natural defenses against bacteria, viruses, and fungi.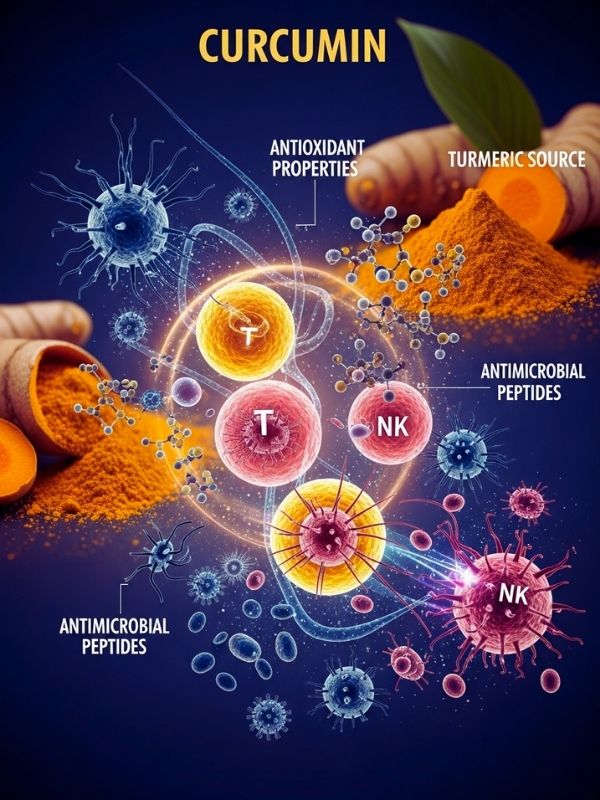
Curcumin also affects the gut microbiome, which is an important part of the immune system. Turmeric helps both the digestive and immune systems by encouraging the growth of good gut bacteria and lowering inflammatory responses in the lining of the intestines. Studies show that curcumin may help the immune system respond better to exposure to antigens, lower the severity and frequency of infections, and improve respiratory health. Adding turmeric to your daily diet helps keep your immune system strong and balanced. This makes your body better able to handle seasonal changes, pathogens, and environmental stressors.
🌱 How Curcumin Protects Cells from Oxidative Stress with Its Antioxidant Defense Mechanism
When free radicals outnumber the body’s antioxidants, oxidative stress happens. This damages cells and speeds up the aging process. Turmeric has a lot of antioxidant compounds that help cells repair themselves by neutralizing reactive oxygen species (ROS). Curcumin boosts the body’s natural defenses by activating antioxidant enzymes like superoxide dismutase (SOD), glutathione peroxidase, and catalase.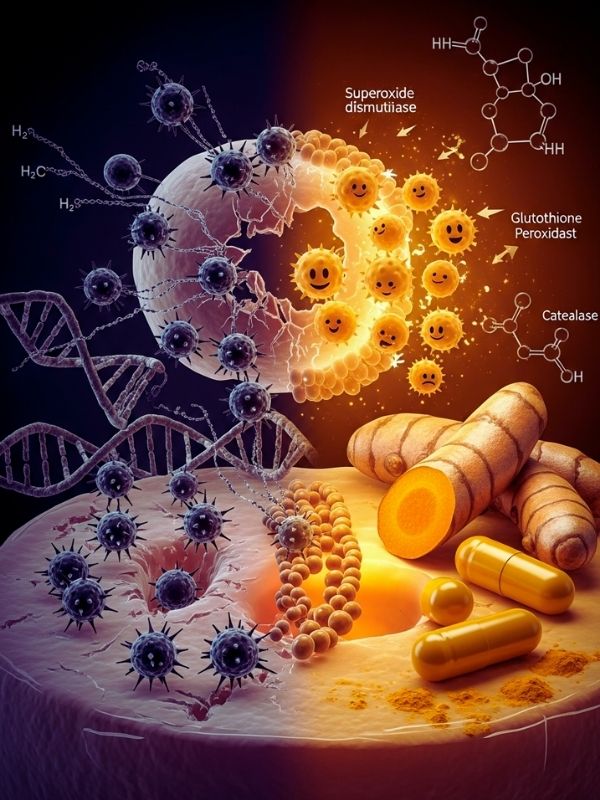
Curcumin’s antioxidant properties help keep DNA, lipid membranes, protein structures, and mitochondrial function safe. This protection is important for long-term health and lowers the risk of chronic diseases linked to oxidative stress, such as cancer, diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and neurological disorders like Alzheimer’s disease. Curcumin can also chelate metal ions like iron and copper, which lowers oxidative damage caused by free radicals that are made when metals are present. This antioxidant defense works in many ways to help the body heal and feel better.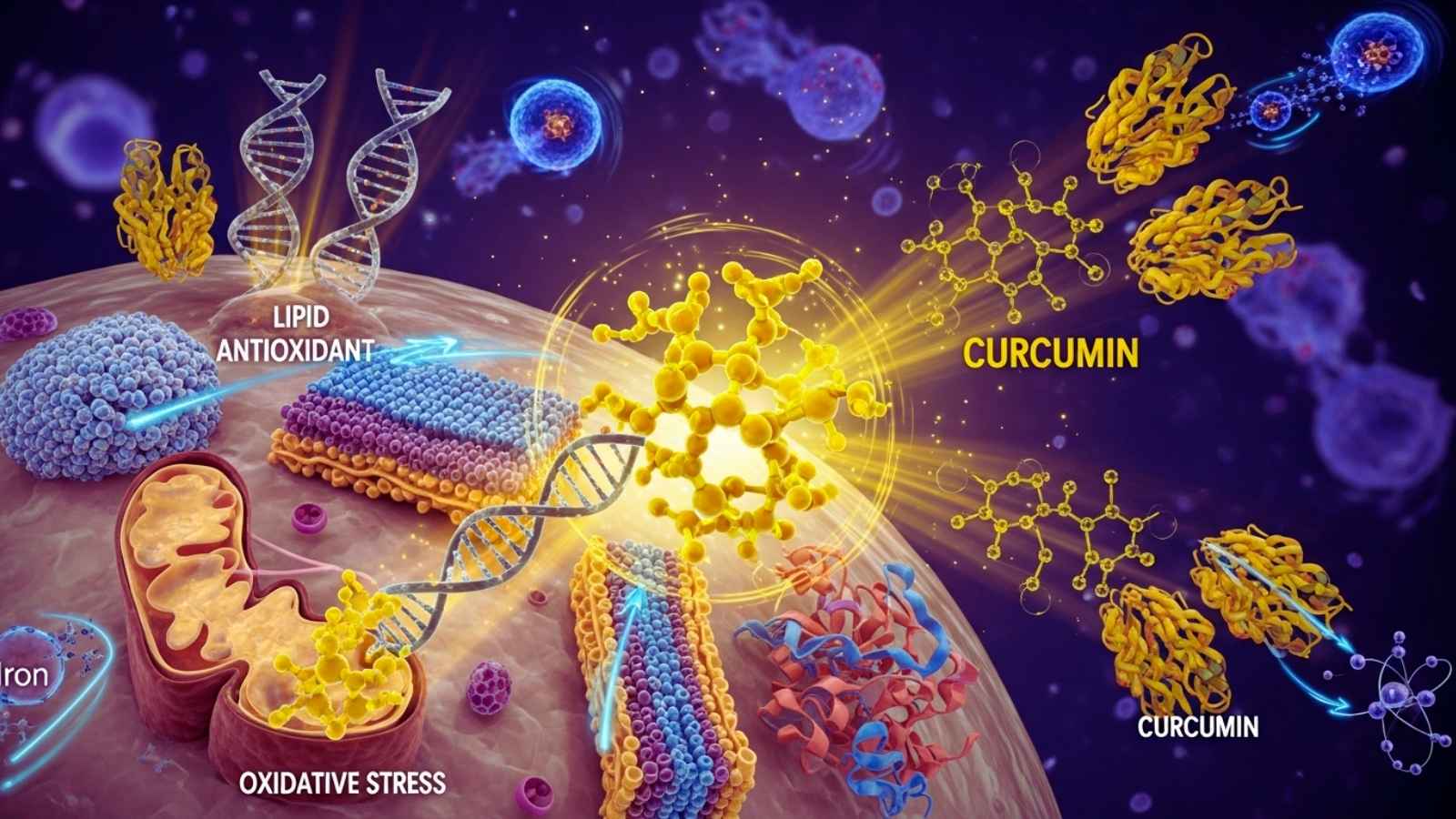
When you eat it, turmeric works with other natural antioxidants like vitamin C, vitamin E, and polyphenols that are found in fruits and vegetables. Eating foods with turmeric, drinking golden milk, or taking curcumin supplements on a regular basis can help the body’s oxidative defense system and keep cells healthy for a long time.
🏞️ Turmeric and Digestive Health: A Natural Way to Balance Your Gut
Taking care of your digestive health is very important for your overall health. People have long used turmeric to help with digestion, ease bloating, and ease stomach pain. Studies in science show that curcumin helps the gut stay healthy by lowering inflammation in the intestines, increasing bile secretion, and keeping the lining of the intestines intact.
Curcumin helps with symptoms of conditions like irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), colitis, and gastritis by reducing inflammation. It helps digestion and nutrient absorption by controlling the makeup of gut microbiota. Turmeric also makes the liver make bile acids, which are important for breaking down fats and helping with digestion. Turmeric helps make the metabolic environment healthier by making the liver work better and lowering oxidative damage.
Turmeric also protects the lining of the stomach from damage caused by stress, alcohol, or drugs. It helps relax the muscles in the intestines and ease stomach cramps because it is an antispasmodic. Adding turmeric to your daily meals can help your digestion work better, make you hungrier, and make your gut healthier.
🌤️ A Natural Way to Relieve Pain: Turmeric for Joint and Muscle Health
As people get older, their joints can hurt and become stiff, and their muscles can become inflamed. This can happen because of stress, autoimmune diseases, or just getting older. Turmeric helps naturally by lowering markers of inflammation and making joints more slippery. Studies show that curcumin is very good at easing the symptoms of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis by lowering synovial inflammation and stopping enzymes that break down joints.
Using turmeric on a regular basis can help ease morning stiffness, swelling, and pain in the joints. It helps with recovery after exercise and lessens delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS) because it relaxes muscles. Turmeric is better for your joints in the long run than synthetic painkillers because it feeds your tissues and doesn’t have any bad side effects. Because of this, it is a popular natural treatment for athletes, older adults, and people with chronic inflammatory conditions.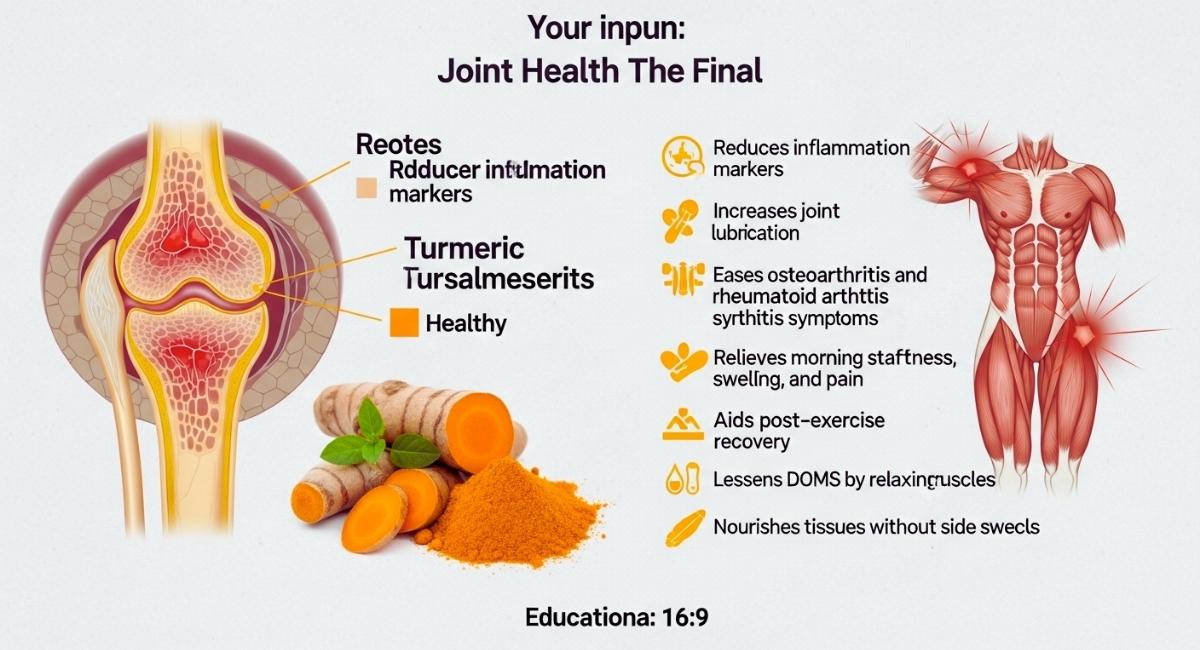
🔬 Conclusion: Turmeric is an important part of daily health
There is scientific evidence and hundreds of years of traditional use that show that turmeric is one of nature’s most powerful healing agents. It is a powerful natural treatment for inflammation, skin health, immunity, digestion, and overall health because it has a lot of curcuminoids, essential oils, and antioxidants. Turmeric is good for the body in many ways, whether you eat it, take it as a supplement, or put it on your skin.
It’s easy to add turmeric to your daily life. You can do this by drinking golden milk, turmeric water, herbal teas, curries, or standardized curcumin extracts. Turmeric is still a great spice for protecting, nourishing, and strengthening the body because it has many healing properties and scientifically proven ways of working. Turmeric is still a powerful natural health and vitality booster, even as research continues to find new ways to use it.
