Aloe vera (Aloe barbadensis miller) is a highly esteemed medicinal plant in traditional healing systems, including Ayurveda, Siddha, Unani, and contemporary herbal therapy.  The thick, fleshy leaves have a clear, slimy gel that is full of bioactive compounds like polysaccharides (especially acemannan), anthraquinones, enzymes, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, sterols, lignin, and saponins. People have called aloe vera the “Burn Plant,” “Miracle Plant,” and “Natural Healer” for hundreds of years because it works so well on skin, hair, and digestion. Aloe vera is one of the most studied natural remedies in the world because modern science has confirmed many of the old claims. In this in-depth article, we look at the science behind aloe vera, how it works, and the real health benefits it has for people, especially for hair growth, skin care, and gut health.
The thick, fleshy leaves have a clear, slimy gel that is full of bioactive compounds like polysaccharides (especially acemannan), anthraquinones, enzymes, amino acids, vitamins, minerals, sterols, lignin, and saponins. People have called aloe vera the “Burn Plant,” “Miracle Plant,” and “Natural Healer” for hundreds of years because it works so well on skin, hair, and digestion. Aloe vera is one of the most studied natural remedies in the world because modern science has confirmed many of the old claims. In this in-depth article, we look at the science behind aloe vera, how it works, and the real health benefits it has for people, especially for hair growth, skin care, and gut health.
• The plant and chemical makeup of aloe vera
Aloe vera is a type of succulent that grows in dry areas of Africa and the Arabian Peninsula. It is a member of the Asphodelaceae family. There are three layers in the leaf structure: an outer green rind (periderm), a middle layer of latex, and an inner clear gel parenchyma. The gel is mostly water (95–98%), but it also has hydrophilic polysaccharides like acemannan, which help it fight infections, heal wounds, and reduce inflammation. Acemannan is a long-chain β-(1,4)-linked acetylated mannose polysaccharide that boosts fibroblast activity, speeds up epithelial regeneration, and boosts collagen synthesis. The latex part has anthraquinone compounds like aloin, aloe-emodin, and barbaloin, which are what make it a strong laxative. However, if you eat too much of it, it can be irritating.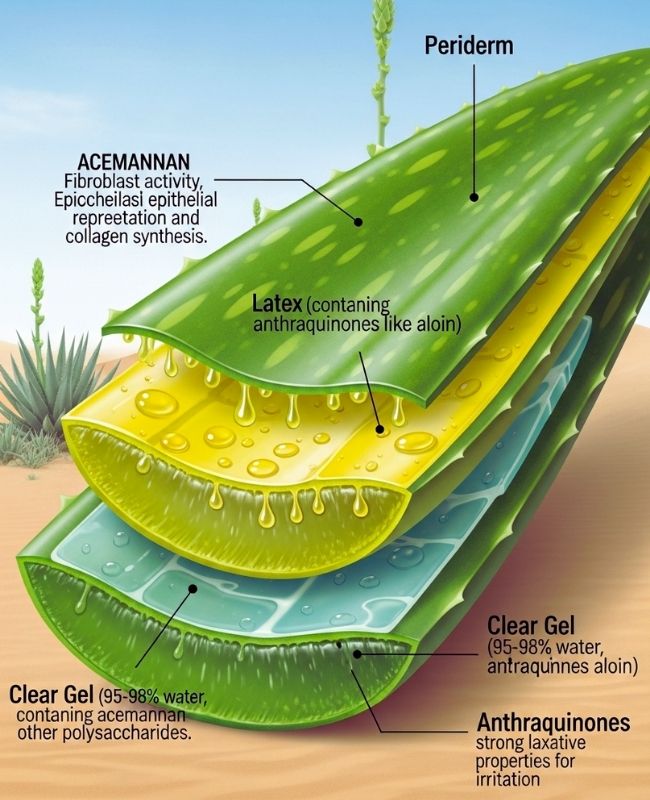 Aloe vera is also a good source of vitamins A (as beta-carotene), C, E (powerful antioxidants), B12, folic acid, and choline. It has minerals like calcium, zinc, copper, magnesium, potassium, and chromium. Amylase, lipase, and cellulase are enzymes that help with digestion, while salicylic acid helps with inflammation and bacteria. This unique biochemical richness is what makes aloe useful for so many different things.
Aloe vera is also a good source of vitamins A (as beta-carotene), C, E (powerful antioxidants), B12, folic acid, and choline. It has minerals like calcium, zinc, copper, magnesium, potassium, and chromium. Amylase, lipase, and cellulase are enzymes that help with digestion, while salicylic acid helps with inflammation and bacteria. This unique biochemical richness is what makes aloe useful for so many different things.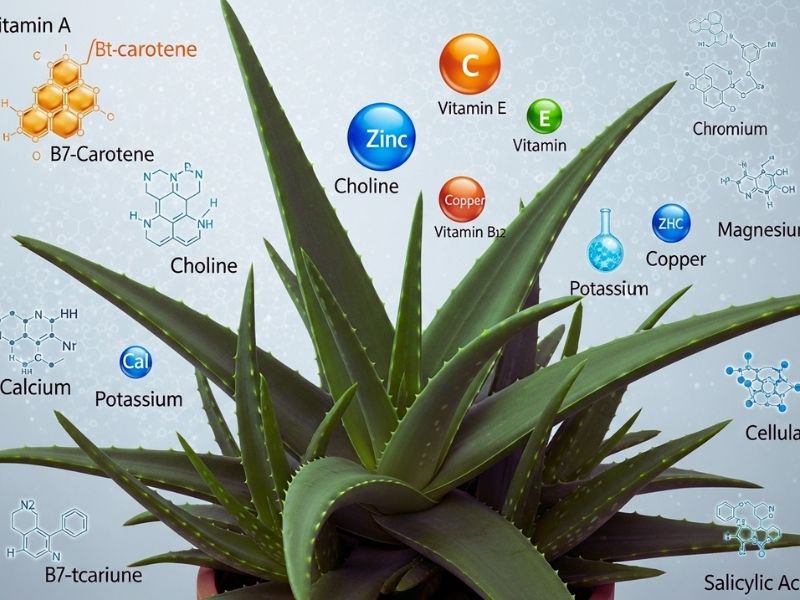
• Aloe Vera for Skin Health: Natural Healing and Benefits for the Skin
Aloe vera is used a lot in dermatology because it heals, moisturizes, and calms the skin. The gel’s humectant effect pulls moisture into the skin and makes the epidermis more hydrated, which is what makes it so hydrating. Because it has a lot of water in it, it makes a great natural moisturizer that doesn’t leave a greasy residue. Aloe’s main polysaccharides form a protective film that helps the skin hold onto moisture and works with the skin’s barrier function.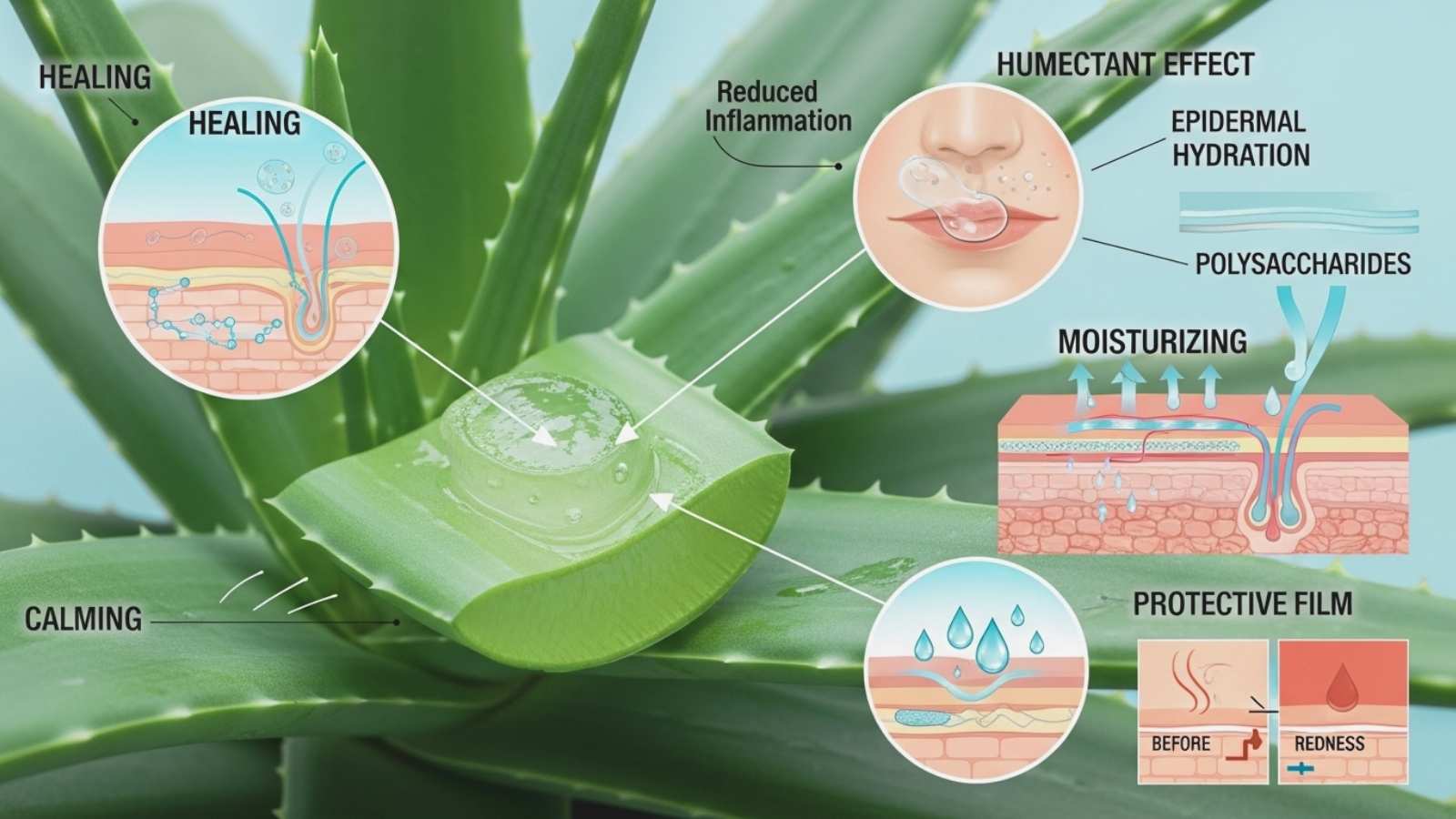
There is scientific evidence that aloe vera can help wounds heal. Acemannan makes fibroblasts grow, which helps make collagen, elastin, and new tissue. This is why aloe vera is so good for cuts, small wounds, burns, and sunburns. Gibberellins and auxins, two plant hormones, help it heal wounds and reduce inflammation. Research indicates that aloe vera diminishes the healing duration of first-degree and second-degree burns by expediting cellular regeneration and enhancing circulation in the impacted regions.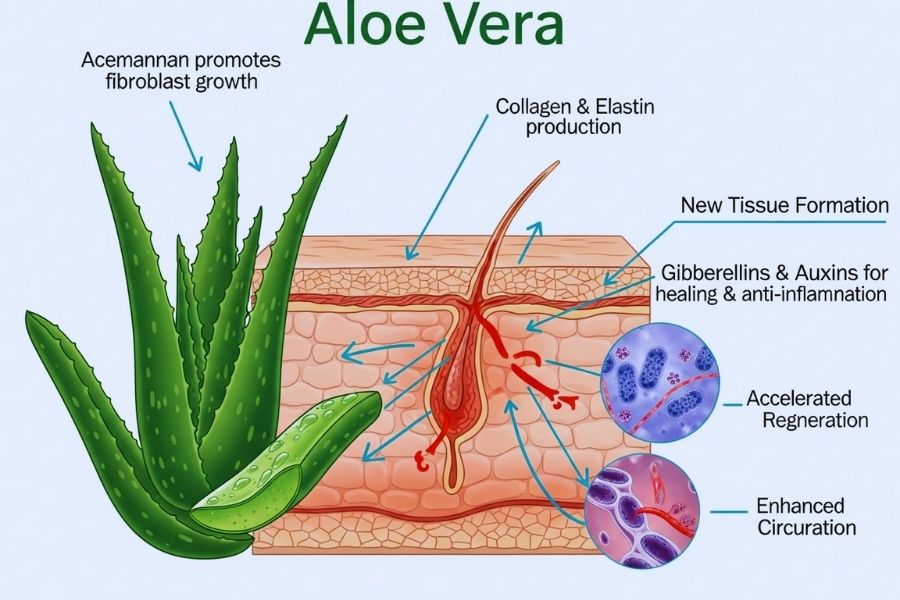
Aloe’s anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties are another big reason why it’s good for your skin. The gel has phenolic compounds and vitamins C and E that fight free radicals, which are what cause oxidative stress and early aging. These antioxidants help your skin look younger by getting rid of wrinkles, fine lines, dark spots, and damage from the sun. Aloe’s ability to reduce inflammation makes it useful for inflammatory skin conditions like acne, eczema, and psoriasis. It also helps with redness, swelling, and irritation. Its antimicrobial properties, especially from compounds like salicylic acid and saponins, help fight bacteria that cause acne and calm down inflamed sebaceous glands, which makes skin clearer.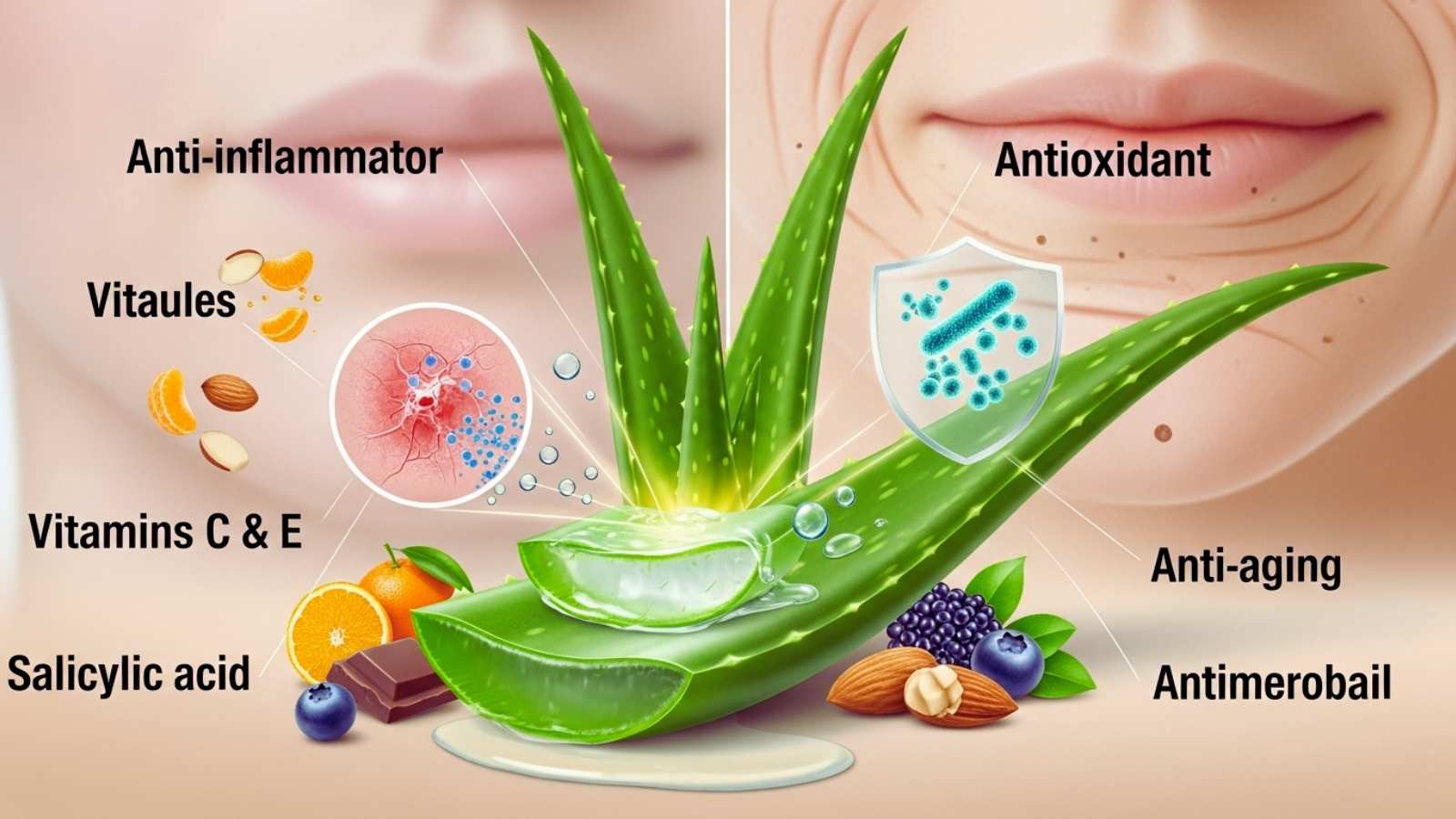
Aloe vera is also known to help skin stay elastic by making collagen cross-linking better and increasing the production of hyaluronic acid. Using it on your skin regularly can slowly make it firmer, smoother, and brighter. Aloe vera is a common ingredient in creams, gels, serums, and sunscreens because it can balance the pH of the skin, reduce irritation, and speed up healing. Aloe is a gentle, natural alternative to harsher chemical-based skincare products for people with sensitive skin.
• Aloe Vera for Hair Care: Growth, Strength, and Health of the Scalp
People have used aloe vera as a natural hair tonic for a long time because it can nourish hair follicles, keep the scalp healthy, and help hair stay strong and shiny. Its proteolytic enzymes help break down dead skin cells on the scalp, clear hair follicles, and help the roots absorb more nutrients. Aloe vera makes a better place for new hair to grow by getting rid of dead keratin buildup.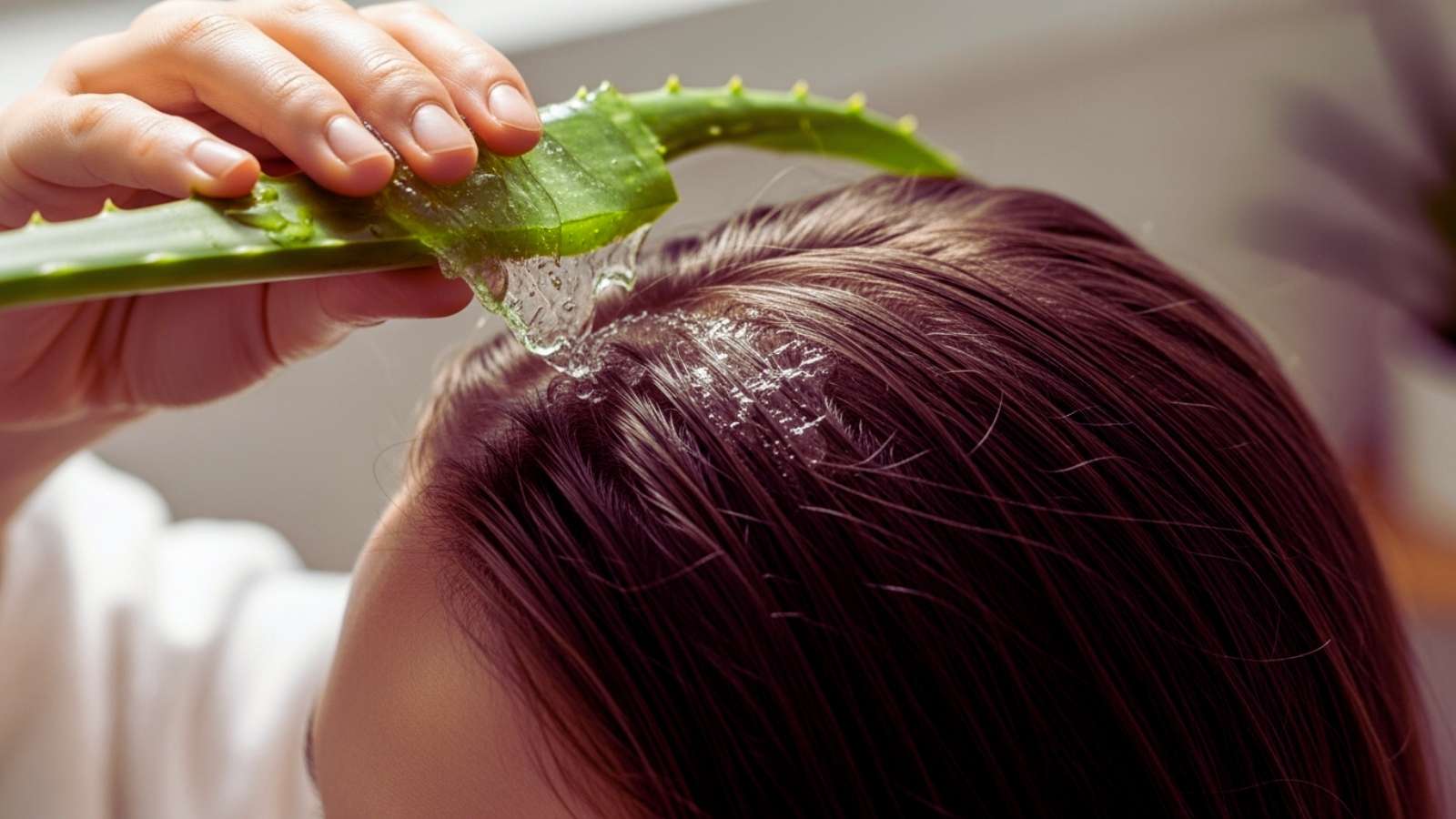
The gel’s ability to fight inflammation and bacteria is good for people with dandruff, seborrheic dermatitis, scalp psoriasis, and fungal infections. Aloe has substances that stop the growth of Malassezia yeast, which is what causes most dandruff. It calms the scalp, which helps with irritation, itching, and flakiness. The polysaccharides in aloe help the scalp hold onto moisture, which keeps it from getting too dry and makes the hair feel better overall.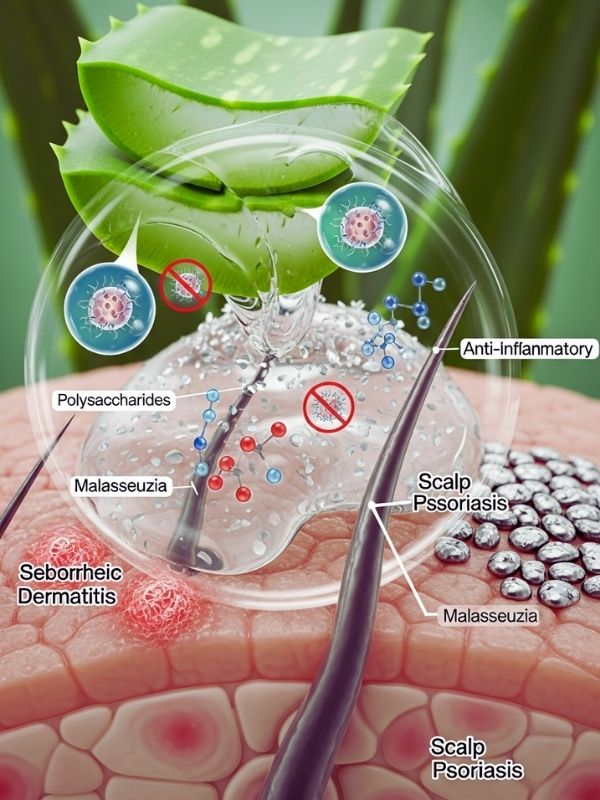
Aloe vera also has structural proteins that are similar to keratin, which is the main protein that makes up hair strands. These proteins help fix broken hair shafts, smooth out cuticles, and stop hair from breaking. It makes hair softer and shinier without using chemical conditioners that can cause buildup.
Better blood flow to the scalp is another scientifically proven benefit. Aloe’s gel is full of nutrients and sends vitamins C, E, and B-complex straight to the roots of the hair, which makes hair follicles work harder and grow faster. It gives hair minerals like zinc and copper, which are important for strong and healthy hair structure, and it makes hair stronger from root to tip. Many herbalists say that using aloe vera gel directly on the scalp before washing it, mixed with oils like coconut or castor oil, will give you even better results.
Aloe vera also keeps the pH of the scalp closer to its natural acidic level (about pH 5.5), which helps protect the hair cuticle and keep hair from getting frizzy, developing split ends, or thinning. When you use aloe vera regularly, it helps your hair become thicker, healthier, and stronger.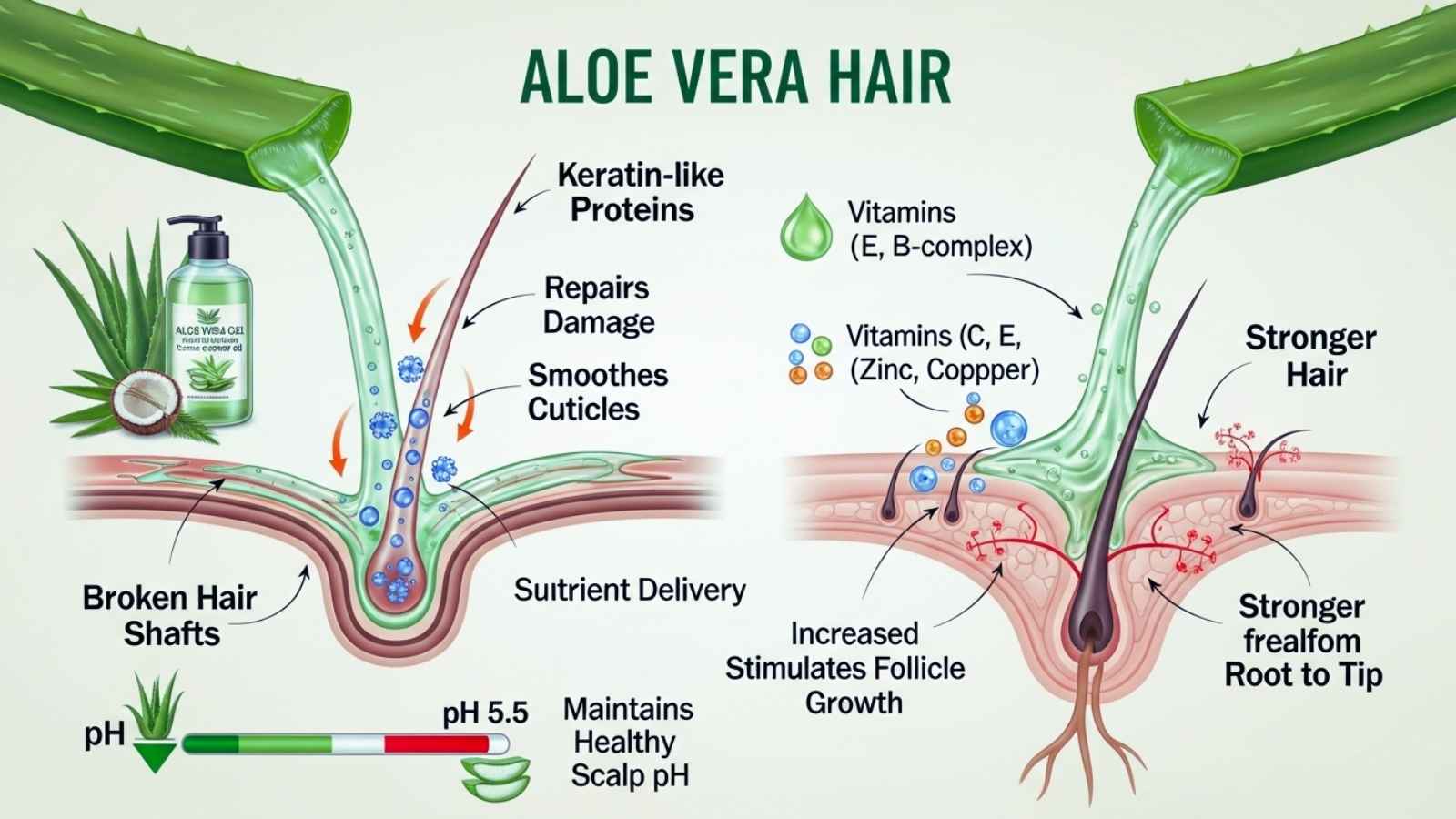
• Aloe Vera for Digestion: Cleansing and keeping the digestive system healthy
Aloe vera is well-known for being good for digestion because it has a lot of enzymes, polysaccharides, and phytochemicals that help keep the digestive system healthy. Its gel inside calms the mucous membranes of the digestive tract and can help treat conditions like acid reflux, indigestion, gastritis, and inflammatory bowel diseases. Acemannan, one of the most important polysaccharides, acts as a prebiotic, which means it helps feed good gut bacteria and makes digestion work better overall.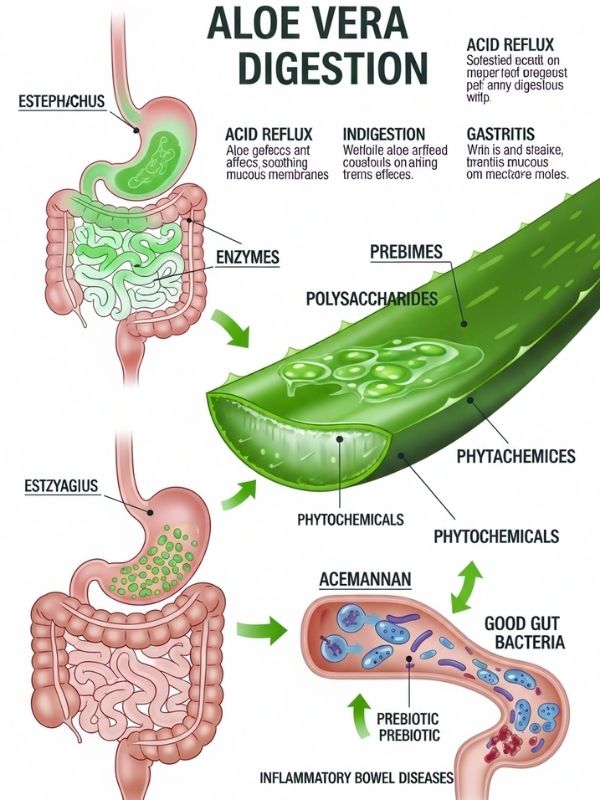
The mucilage in aloe vera protects the stomach lining, which helps heal gastric tissues faster and reduces irritation caused by too much acid. This makes aloe especially helpful for people who have GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease) or chronic gastritis. Aloe’s anti-inflammatory properties help calm inflammation in the digestive tract, which makes it easier for food to move through and lessens stomach pain.
Aloe’s mild laxative effect is another important benefit for digestion. Aloe latex has anthraquinone glycosides like aloin and emodin in it. These glycosides make the intestine move in a wave-like way, which helps keep bowel movements regular. Aloe can help with constipation by making the intestines hold more water and making it easier for stool to pass when taken in controlled amounts. But you shouldn’t use aloe latex for a long time because it can cause an electrolyte imbalance and irritate the intestines. Aloe vera gel (without latex) is safe and helps with digestion in a gentle way without being a strong laxative.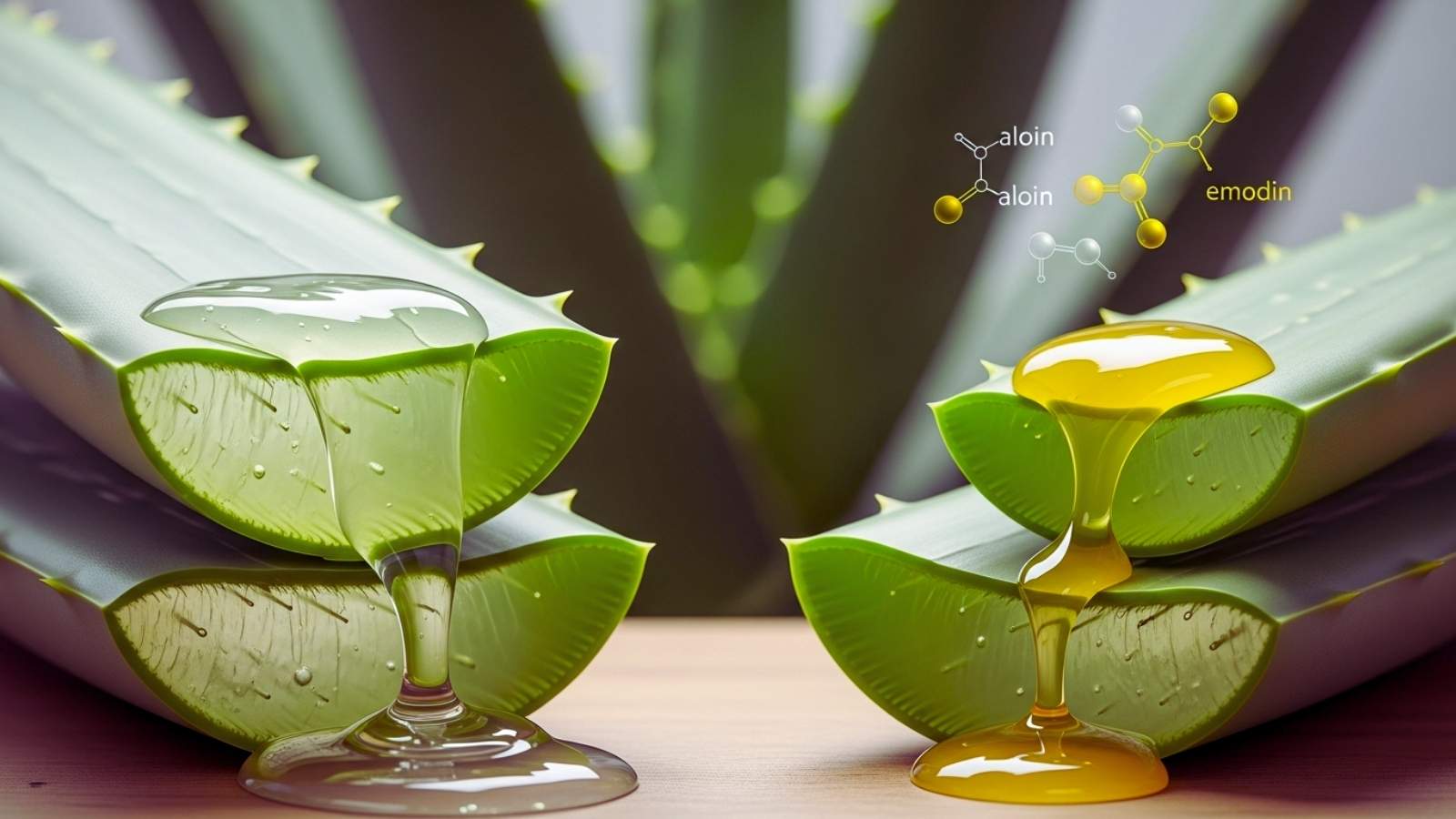
Aloe vera also helps get rid of toxins. Its antioxidants help the liver detoxify and protect it from oxidative stress. Aloe is good for the health of the whole digestive system because it speeds up metabolic processes and helps the body absorb nutrients better. Drinking aloe vera juice regularly (after removing aloin) may help make your bowels more regular, boost your gut’s immune system, and create a healthier environment for microbes.
Scientific studies also show that aloe can help with irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) symptoms like bloating, stomach pain, and not going to the bathroom regularly. It helps people with inflammatory bowel diseases like ulcerative colitis because it is soothing and anti-inflammatory. However, more research is needed to find the right dose for everyone.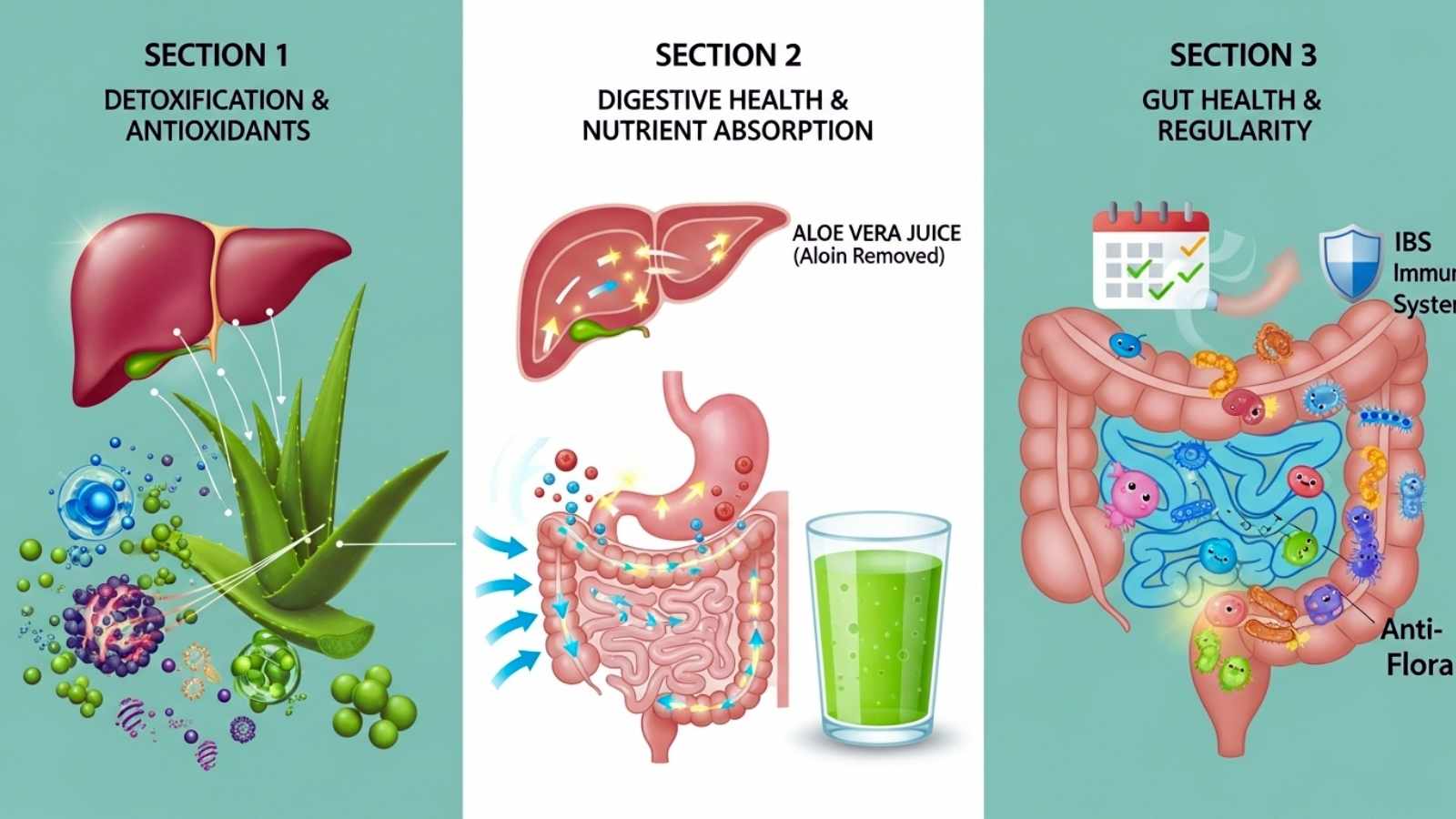
• Aloe Vera’s Antimicrobial, Antioxidant, and Anti-inflammatory Effects
Aloe vera has a lot of healing power because it has strong anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. There are more than 75 bioactive compounds in the plant, such as chromones, flavonoids, and anthraquinones, which are phenolic antioxidants. These substances stop free radicals from damaging cells and making them age too quickly. Vitamins C and E make this antioxidant effect stronger by lowering oxidative stress, speeding up tissue healing, and boosting the immune system.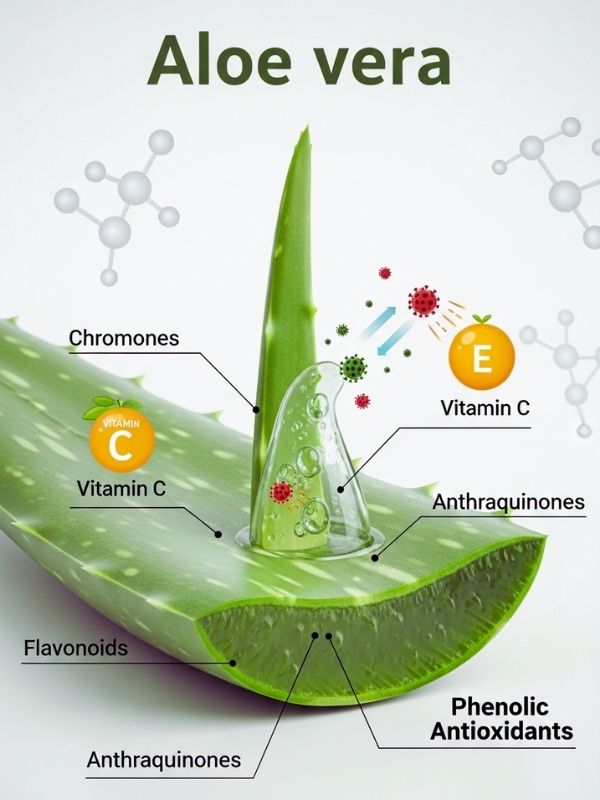
Bradykinase (an enzyme that reduces too much inflammation), C-glucosyl chromone, salicylic acid, sterols, and polysaccharides that stop inflammatory mediators are some of the compounds that make aloe anti-inflammatory. These compounds stop the cyclooxygenase (COX) pathway, which lowers the production of prostaglandins. Prostaglandins are important because they help relieve pain, swelling, and redness in both skin and internal tissues.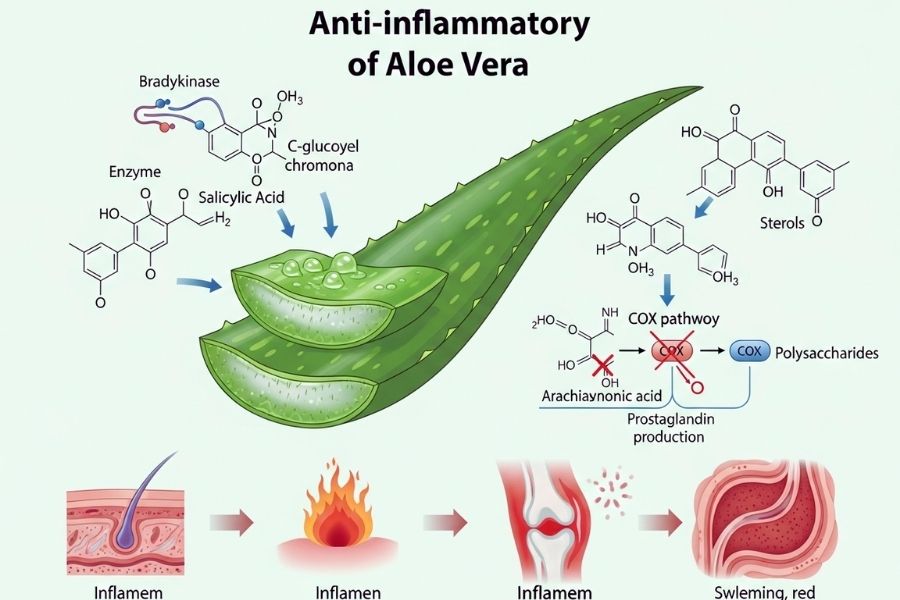
Aloe vera is good at killing bacteria like Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Escherichia coli because it has antimicrobial properties. Anthraquinones, sulfur compounds, and saponins in the plant break down bacterial cell walls. This makes aloe a good natural alternative to chemical antiseptics. Laboratory studies have also shown that it can fight viruses and fungi, especially the ones that cause skin and scalp infections.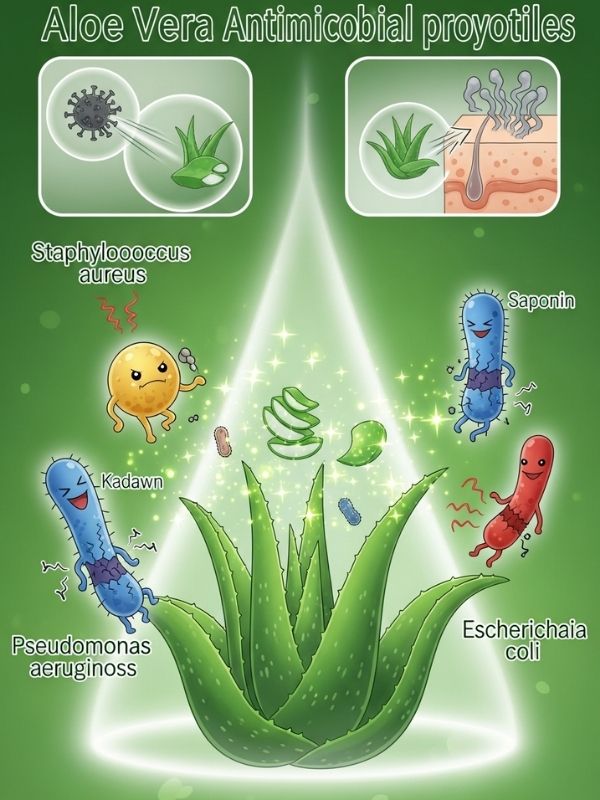
Aloe vera is often used in topical products for wound care, minor infections, and fungal infestations because it has many different pharmacological properties. Aloe is very useful in natural medicine because it has three healing effects: it fights germs, reduces inflammation, and protects cells from damage.
• How Aloe Vera Helps Your Immune System and Metabolism
Aloe vera has a number of substances that change how the immune system works. This helps the body fight off infections and keep its metabolism in balance. Acemannan, the main immunomodulatory polysaccharide, boosts the body’s natural defenses by activating macrophages and improving cytokine secretion. Aloe vera strengthens immune surveillance by stimulating white blood cells, which makes it easier for the body to find and kill pathogens.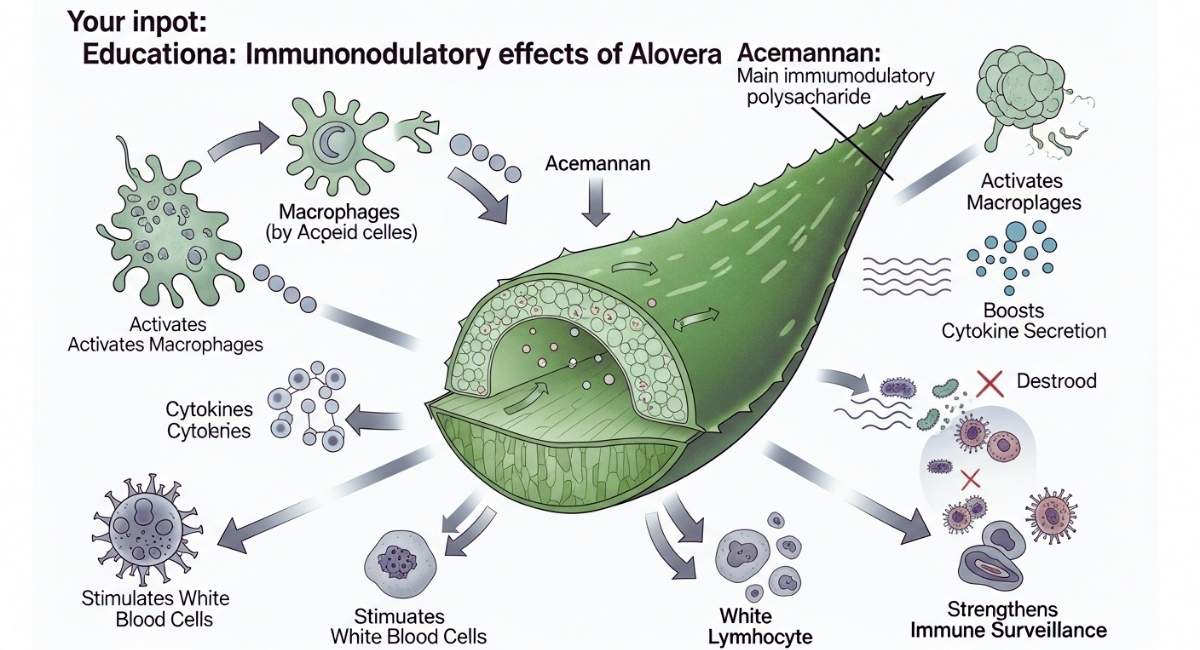
Aloe vera also helps with metabolic health because it has antioxidants. Oxidative stress is a big cause of long-term illnesses like diabetes, atherosclerosis, and disorders that are caused by inflammation. Aloe’s phenolic compounds help lower oxidative markers and improve metabolic function. Research indicates that aloe vera may assist in regulating blood glucose levels by increasing insulin sensitivity and enhancing glucose metabolism when ingested in regulated amounts.
The plant also has small amounts of chromium, magnesium, and manganese, which may help metabolic enzymes work better. Aloe vera should not be used instead of medicine, but it can help your health when used properly.
• Safety, precautions, and suggested use
When used correctly, aloe vera is usually safe to use on the skin and inside the body. Topical application hardly ever causes side effects, except in people who are allergic to aloe, which is rare. Before using any new aloe-based skin care products, always do a patch test. Aloe vera gel should be cleaned up to get rid of aloin before using it inside, especially for people who have sensitive stomachs.
Aloe latex (the yellow sap under the leaf skin) should not be used by pregnant women, menstruating women, dehydrated people, or people with kidney problems because it is a strong laxative. Too much of it can cause stomach cramps, diarrhea, and an imbalance in potassium. Aloe vera juice (decolorized and aloin-free) is safe to drink in moderation for regular health maintenance.
• Conclusion: Aloe vera is a natural gift for healthy skin, hair, and digestion
Aloe vera is still one of the most powerful medicinal plants in the world. It has been shown to be good for the skin, hair, and digestive system. It has a lot of different phytochemicals, like acemannan, anthraquinones, vitamins, minerals, enzymes, and amino acids, which give it strong healing, anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, and antimicrobial properties. Aloe vera has a lot of different health benefits, such as healing skin, promoting hair growth, calming the stomach, and improving digestion.
Aloe vera is an important part of herbal health routines because it can greatly improve overall health when used regularly and responsibly. As more research backs up its traditional uses, aloe vera remains a strong, natural, effective, and easy-to-find solution for everyday health.

